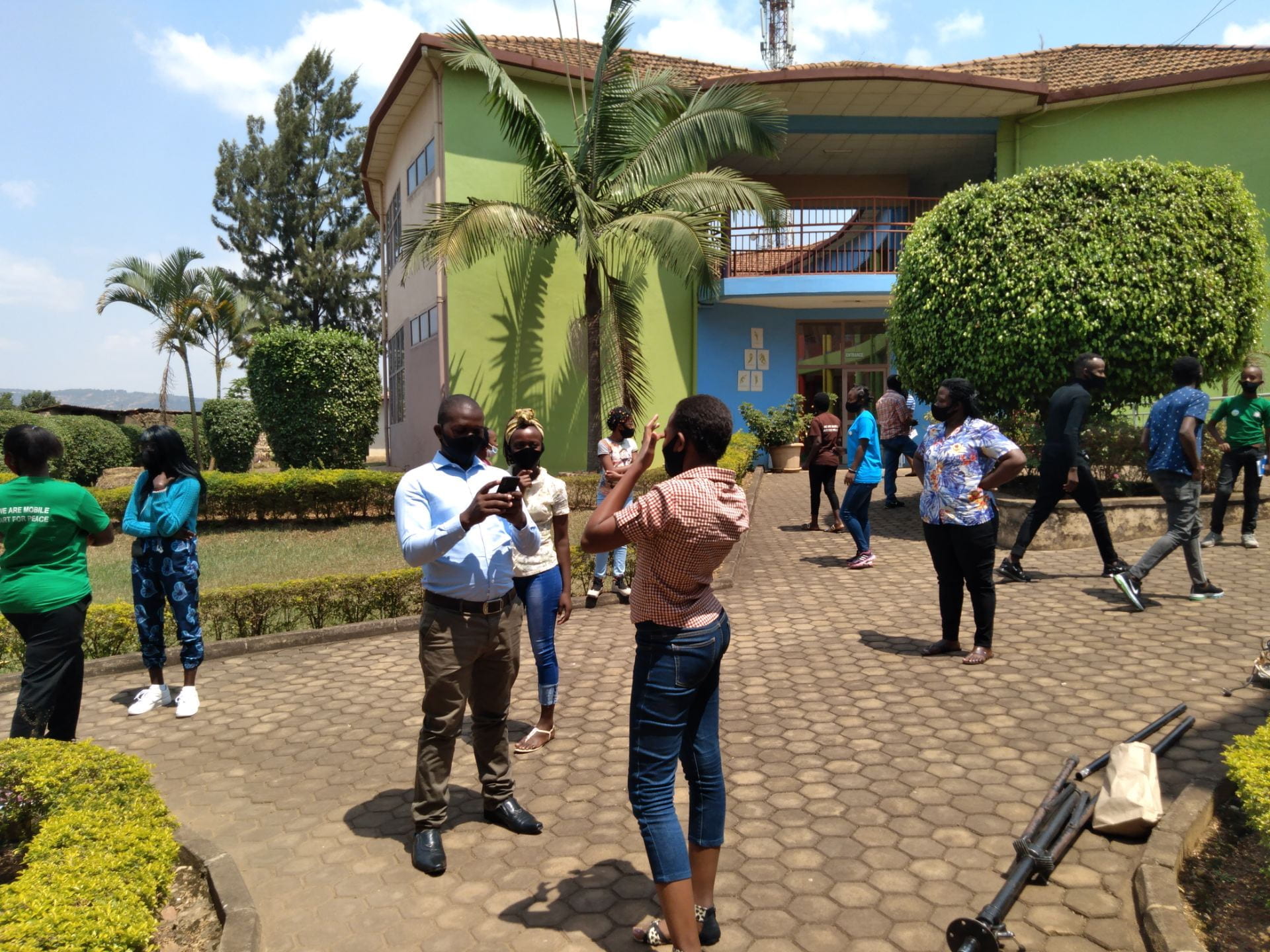Latest posts
- Policy documents: UNICEF Innocenti Discussion Paper on Children and Youth Participation (August 2025) 26 August 2025
- MAP International Online Conference 2025: Session Summaries Report 24 July 2025
- MAP 2025 Conference Highlights: Recordings and Slides 23 July 2025
- Journal article: Reimagining Peace Education in Nepal: Arts-Based, Learner-Centric Pedagogy for Social Justice and Equity 13 July 2025
- Curricula: Mithila art-focused local curriculum in Nepal 2 July 2025
- MAP International Online Conference 2025 1 June 2025
- Policy brief: Gira Ingoma book and policy brief: “The Culture We Want, for the Woman We Want” 28 November 2024
- Manuals and toolkits: GENPEACE Children’s Participation Module in the Development Process 13 November 2024
- Journal article: [Working Paper] Gira Ingoma – One Drum per Girl: The culture we want for the woman we want 30 October 2024
- Curricula: Beyond Tradition: Psychosocial Model 30 October 2024
- Curricula: Beyond Tradition Module: Revitalizing Lenong as a Model for Teaching Betawi Arts 30 October 2024
- Curricula: Beyond Tradition: Lenong Revitalisation as a Model for Teaching Betawi Cultural Arts 30 October 2024
Beyond voice: expressing youth agency through arts-based approaches in Mobile Arts for Peace (MAP)
Written by Di Wu
A 3-day event was hosted by the Mobile Arts for Peace (MAP) and Changing the Story (CTS), in collaboration with the Institute of Research and Dialogue for Peace (IRDP) in Rwanda. The event aimed at using art-based approaches to engage young people, educators, cultural artists and policy makers to influence curriculum and policy-making for peacebuilding. The event provided a rich and dynamic platform that enabled participants from Rwanda, Kyrgyzstan, Indonesia, Nepal, Cambodia, Ugand, and other countries to actively build conversation, share ideas and find solutions by addressing the young people’s theatre play, story-telling and other art-based activities despite the time and geographical differences across the countries as well as the limited conditions caused by Covid-19.
As the founder of MAP Professor Ananda Breed said, “in terms of the projects, there is building of art skills, creative thinking, well being and a space or environment in which young people feel abled to share stories in a deep and meaning ways and apply their stories to influence others, to find solutions to those problems in their community.” In other words, the project enables young people to voice their views and assert their agency through creative and expressive means. In the study of childhood, children and young people are recognized as ‘voiceless’ due to the lack of power and their minor position in relation to adults. It is true that children and young people are restrained by the limited platforms to express their voices. Even though they increasingly participate in different programs, organizations and governments due to the promotion of children’s rights, there is still a gap between practice and policy and the programs are often “tokenistic, unrepresentative in membership, adult-led in process, and ineffective in acting upon what children want”. [1]
Portraying children and young people as ‘voiceless’ tends to neglect the fact that they are able to utilize art tools, such as theatre play, story telling and music to expressing their agency in creative, articulate and meaningful ways and therefore to negotiate their position in adult-dominant world and actively engage in the political arenas. [2] Through a series of activities including a curriculum workshop, training of trainers and drama clubs organized by MAP, children and young people are expected to be at the centre, voicing their everyday lives in the complex social and cultural contexts through bodily actions, theatre and musical performance and other creative methods in order to build dialogue, influence and challenge their relationships with parents, communities and wider social structures. MAP Rwanda youth trainer Sandrine said that there was a big difference between before and after engaging with MAP. Before being part of MAP, she was a very fearful person who could not stand in front of people. After engaging with MAP, she feels free and can stand in front of people and express her ideas clearly.
The MAP methodology also ensures that the adult educators are able to better understand their students from a new perspective and therefore develop and improve the curriculum and learning environment accordingly. A MAP research participant from Rwanda stated that he used MAP activities including drama plays to prepare lesson plans and learners were more motivated and interested. Those activities enable young people to find ways to solve their own problems that are there in society; to clarify the root causes, the consequences, and to find solutions. It is through that platform that the school principals know the problems students have and they try to search for the solutions together.
So far, MAP has reached 250 educators and 2,000 young people in Rwanda and more educators, youth facilitators and students in Kyrgyzstan, Indonesia and Nepal. The MAP approach provides creative means for young people to express concerns and ideas through multiple methods t and to be heard, which therefore builds dialogue among young people, trainers, communities and policy makers to identify and find solutions for peacebuilding.
****
[1] Taft, J. K. (2015). “Adults talk too much”: Intergenerational dialogue and power in the Peruvian movement of working children. Childhood, 22(4), 460-473.
[2] Emberly, A., & Davhula, L. A. (2016). My music, my voice: Musicality, culture and childhood in Vhavenda communities. Childhood, 23(3), 438-45